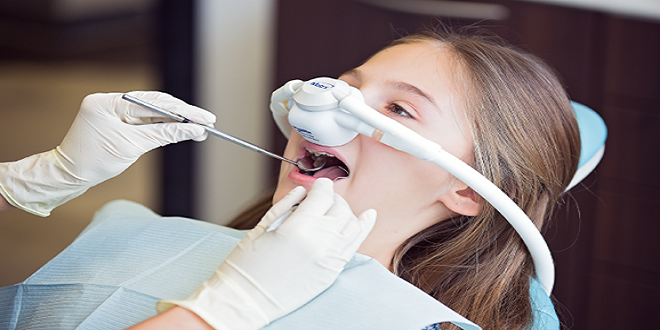
Laughing gas (nitrous oxide) can be useful in a variety of dental situations, including relieving anxiety, keeping children calm during lengthy procedures, and reducing gag reflexes. It is a common and safe sedative in dentistry. However, understanding its applications and potential risks from a dentist at coral gables sedation dentistry is critical for a successful dental visit.
Nitrous oxide:
Nitrous oxide, also known as laughing gas, is a mild sedative that is used in dentistry to alleviate pain and anxiety.
It induces a relaxed state when inhaled through a mask, making you feel calm and comfortable during the procedure. Contrary to its name, it does not always cause laughter, but it can cause dizziness and tingling sensations.
Is it safe and effective?
Yes! Laughing gas (nitrous oxide) is a safe and effective method of sedation that induces relaxation quickly during dental procedures. Its effects wear off quickly with pure oxygen administration, allowing you to remain conscious and responsive to the dentist.
Laughing gas side effects are uncommon, but they might happen if the levels are too high or change too quickly. Headaches, shivering, sweating, nausea, and sleepiness are all possible side effects.
Patients are given oxygen for at least five minutes after use to avoid discomfort and promote alertness. Light eating before and after the procedure can help reduce nausea.
What is it usually used for?
Patients who are fearful, anxious, uncooperative, have special health care needs, sensitive gag reflexes, or do not respond well to local anesthesia are given laughing gas (nitrous oxide). As recommended by the American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry (AAPD), it is also beneficial for younger patients undergoing lengthy dental procedures.
Is it safe for children?
According to the American Academy of Pediatrics, nitrous oxide is generally safe for children. It is simple to adjust, and many children enjoy the sensation of tingling or warmth. It is useful for procedures that require stillness, but wearing the mask may cause nausea or discomfort in some cases. Before undergoing dental treatment, discuss sedation options with your child’s dentist.
Final thoughts:
Although laughing gas tends to be safe and effective, some people may be unable to use it due to medical conditions. Pregnancy in the first trimester, respiratory illnesses such as COPD, vitamin B-12 deficiency, substance abuse history, and mental health conditions are all risk factors, according to the AAPD. Talk to your dentist about your options for your next appointment or operation.
 Magazine Today
Magazine Today